Appearance
What is an integrated motor?
Integrated drive control motors, with their high level of integration, compatibility, convenience, and excellent performance, have become a shining star in modern industrial automation. They are undoubtedly an ideal choice for users seeking efficient, precise, and intelligent control.
The core definition of integrated motor
As the name suggests, an integrated motor is a servo system that integrates components such as a motor, encoder, and driver. It can support buses such as EtherCAT, CANopen, and Modbus.
Simply put, it's like the difference between a desktop computer and a laptop.
Therefore, their compact size easily evokes the need for complex configurations like a driver, encoder, and brake (some products have built-in brakes). They are particularly suitable for space-sensitive and distributed control applications.
According to the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standards, its typical characteristics include:
- Modular design: The motor body shares a common housing with the inverter, encoder and other components, reducing external wiring
- Intelligent control: built-in PLC or IoT interface, supporting real-time parameter adjustment(IEEE 2025 Smart Motor Technology White Paper)
Common combination types of integrated motors
According to the above, we know that the integrated motor includes components such as motor, encoder, and driver. Therefore, according to the different structures of the integrated motor, different classification names are generated, such as integrated stepper motor, integrated servo motor and other combination types.
Integrated stepper motor

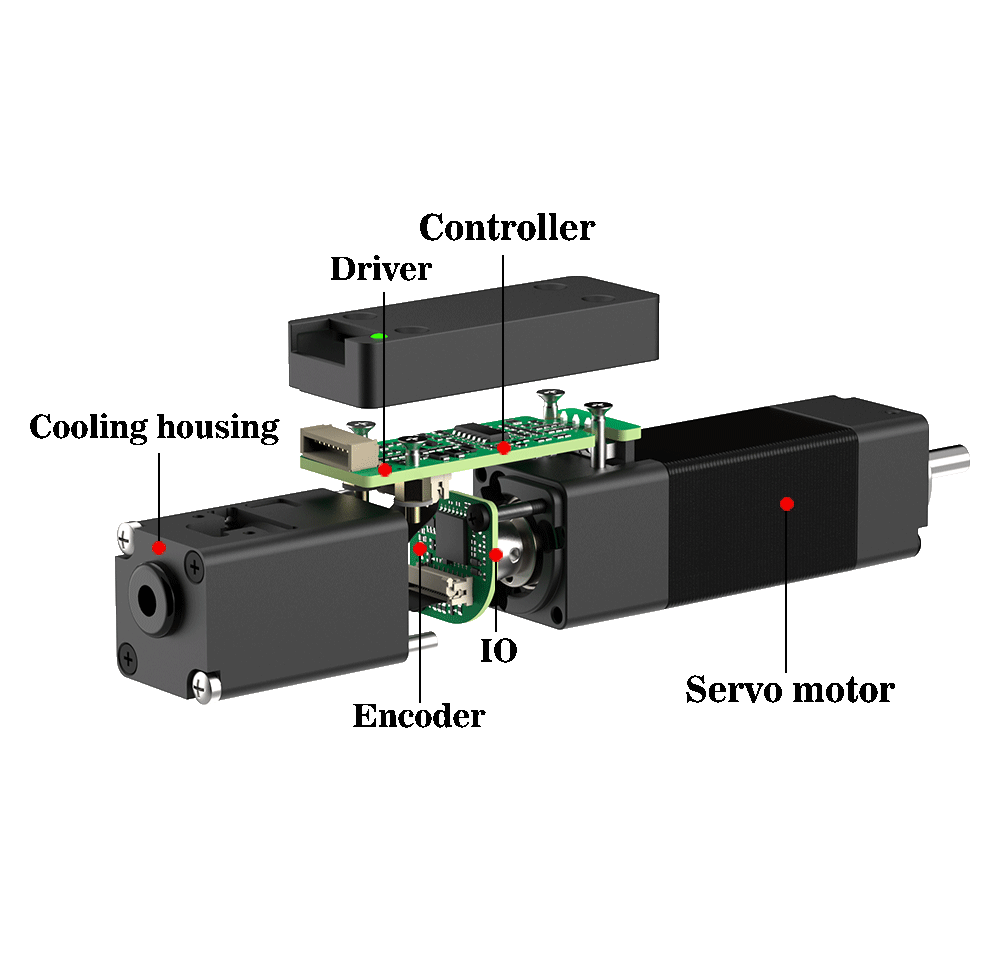
The integrated stepper motor is an intelligent drive unit that integrates the stepper motor, drive circuit and encoder into one, with open-loop or closed-loop control mode.
Generally, they support pulse or bus communication (such as CAN/Modbus/EtherCAT). Their advantages include plug-and-play, space saving (over 40% less than split-type), and real-time position feedback (accuracy of ±0.05°), making them suitable for automation equipment and other applications requiring high-precision positioning (such as 3D printing).
Integrated servo motor
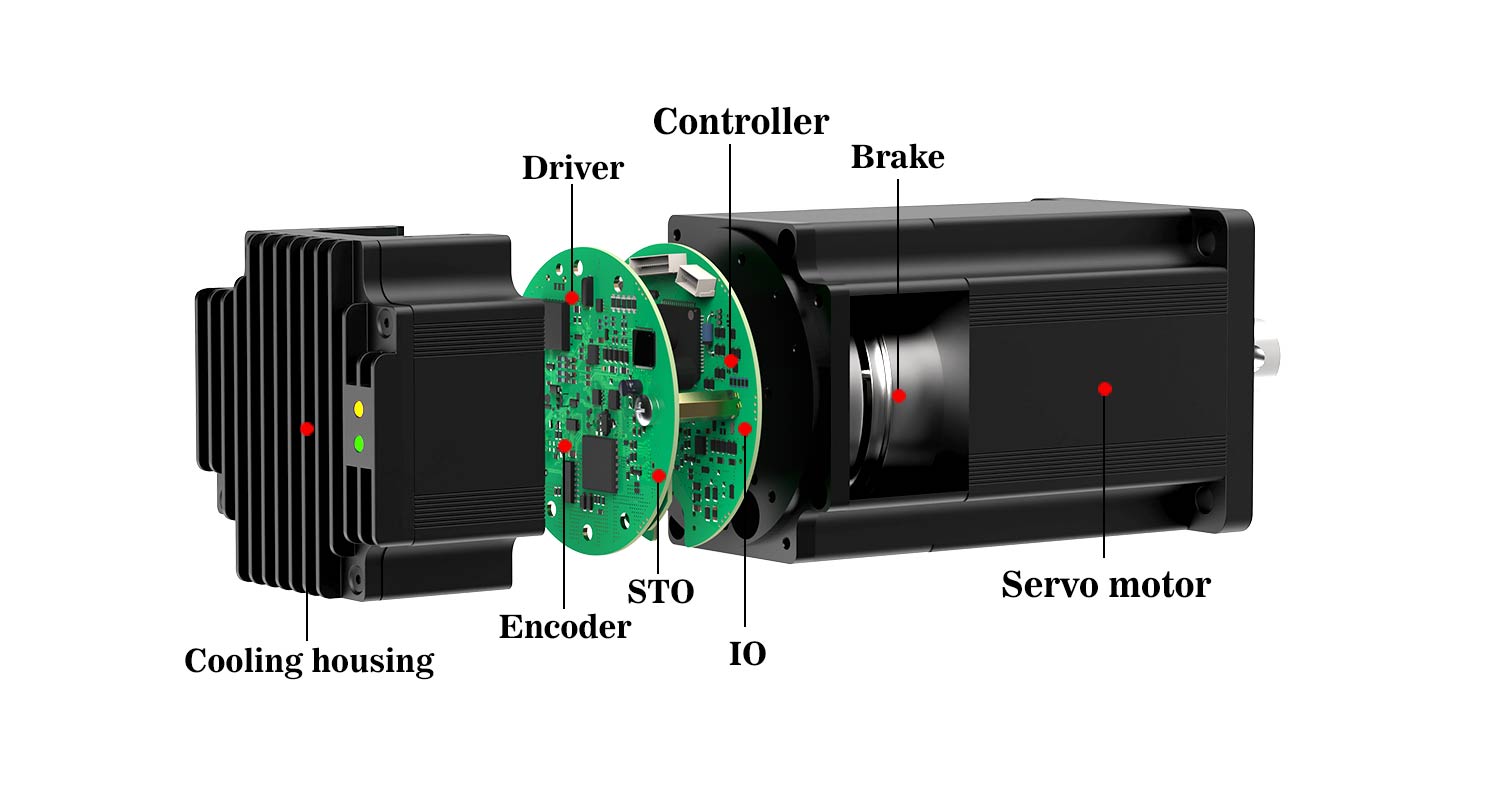
 Integrated servo motors and integrated stepper motors are nearly identical, both consisting of a motor, drive, and encoder. The main difference is that integrated servo motors are based on permanent magnet synchronous motors, drives, and encoders.
Integrated servo motors and integrated stepper motors are nearly identical, both consisting of a motor, drive, and encoder. The main difference is that integrated servo motors are based on permanent magnet synchronous motors, drives, and encoders.
Furthermore, the performance specifications of the drive and encoder are higher than those of integrated stepper motors. Therefore, integrated servo motors offer higher performance than integrated stepper motors, but also come at a higher cost. Integrated servo motors sometimes also include additional components, such as brakes, IP65 protective housings, and STO protection circuits.
The integrated servo motor is a high-precision motion control unit that integrates the servo motor body, driver and encoder into one. It has significant advantages such as small size (47% less space than the traditional split type), simple wiring and fast response speed.
Integrated brushless motor
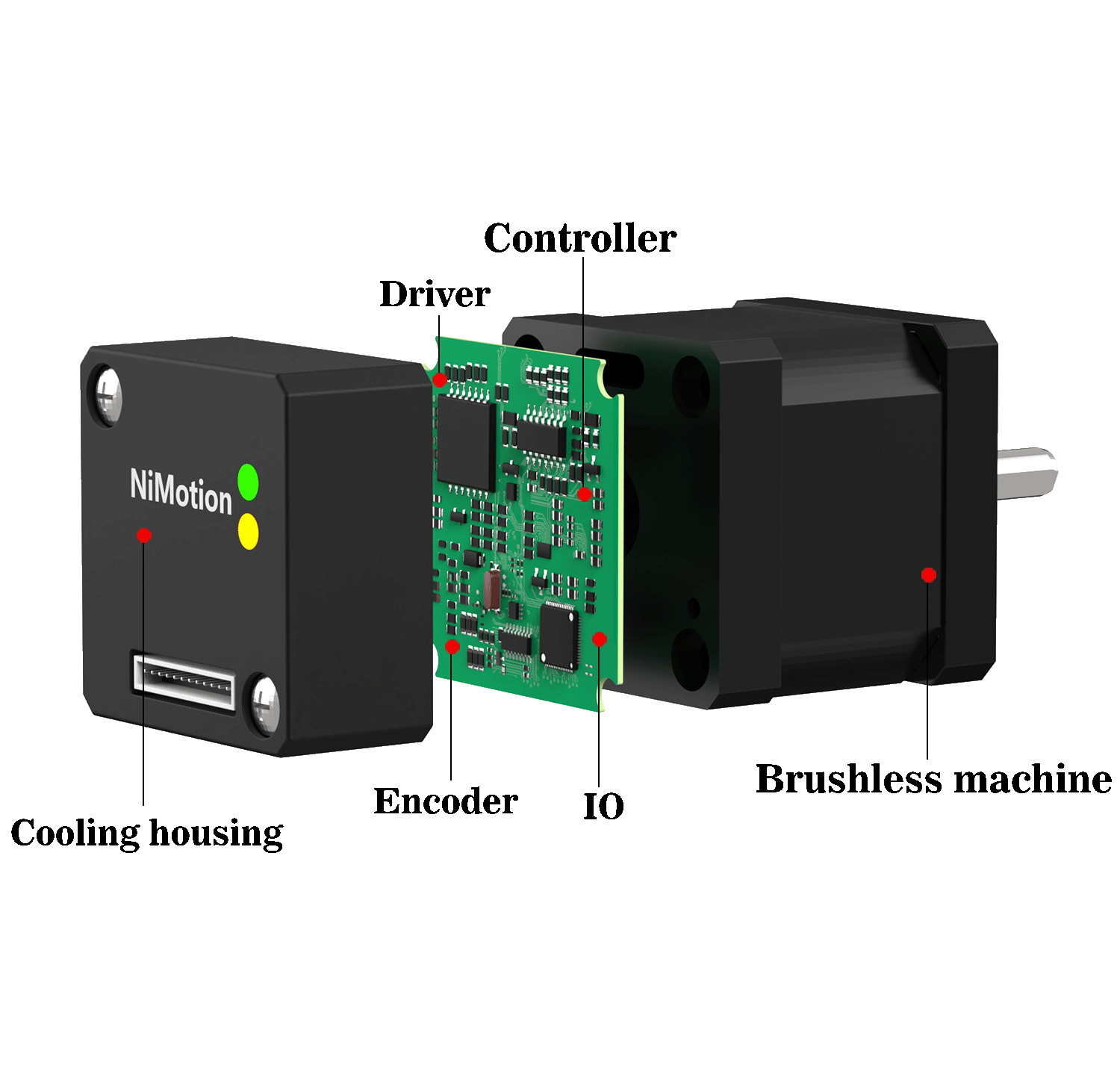 Similarly, the structure of the integrated brushless motor is similar to that of the integrated servo motor. The main difference is that the motor body is an excitation brushless motor. Although the function is the same as the integrated servo motor, the overall performance is worse.
Similarly, the structure of the integrated brushless motor is similar to that of the integrated servo motor. The main difference is that the motor body is an excitation brushless motor. Although the function is the same as the integrated servo motor, the overall performance is worse.
However, its performance is higher than that of the integrated stepper motor, so it is often used to replace the integrated servo motor because of its lower cost and high performance.